by Leipzig University – Phys.org
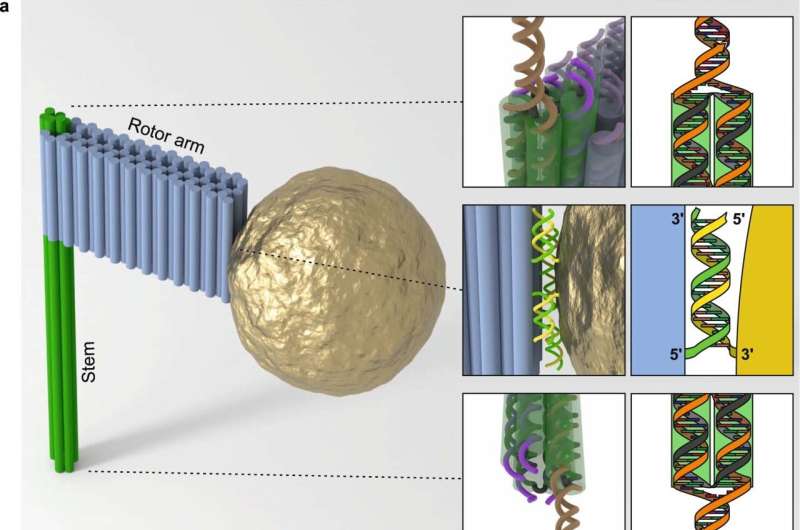
When bacteria are attacked by a virus, they can defend themselves with a mechanism that fends off the genetic material introduced by the intruder. The key is CRISPR-Cas protein complexes. It is only in the last decade that their function for adaptive immunity in microorganisms has been discovered and elucidated.
With the help of an embedded RNA, the CRISPR complexes recognize a short sequence in the attacker’s DNA. The mechanism of sequence recognition by RNA has since been used to selectively switch off and modify genes in any organism. This discovery revolutionized genetic engineering and was already honored in 2020 with the Nobel Prize in Chemistry awarded to Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer A. Doudna.